Socio-economic development of the regions in the Republic of Azerbaijan
Gambarova R.M.1
1 Azerbaijan State Agrarian University
Скачать PDF | Загрузок: 1
Статья в журнале
Креативная экономика (РИНЦ, ВАК)
опубликовать статью | оформить подписку
Том 16, Номер 4 (Апрель 2022)
Цитировать:
Gambarova R.M. Socio-economic development of the regions in the Republic of Azerbaijan // Креативная экономика. – 2022. – Том 16. – № 4. – С. 1651-1659. – doi: 10.18334/ce.16.4.114507.
Эта статья проиндексирована РИНЦ, см. https://elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=48447179
Аннотация:
Since the restoration of state independence of the Republic of Azerbaijan in the late twentieth century, radical changes have taken place in the socio-political and socio-economic life of the country. The purposeful policy pursued in the first years of independence overcame the political and economic crisis in the country and paved the way for Azerbaijan to move forward on the path of building a democratic state and a market economy. The article contains information on the growth rates of the country\'s economy, analysis of key macroeconomic indicators, regional development and investment.
Ключевые слова: economic growth, regional development, investment, socio-economic development
JEL-классификация: R11,R12, R13
В издательстве открыта вакансия ответственного редактора научного журнала с возможностью удаленной работы
Подробнее...
Introduction.
Regional development is the label of the efforts to develop certain areas of a country, with development usually understood in the socioeconomic sense. Regional development is thus not only measured in incomes, the number of jobs, and demographic trends in a certain area, but it can also point to the more general dynamics such as innovation and creativity in the region in focus. [1]
The socio-economic development of each region depends primarily on its natural resources, different economic conditions and production opportunities. The unequal distribution of resources by region is one of the main factors in establishing relations between the regions.
To this end, industries and productive forces must be effectively located in the regions, and the territorial concentration of production and its level of specialization must be ensured. The proper use of labor resources is of paramount importance for the efficient organization of industries in the territory. The main goal of the reforms was to build an independent state with a democratic and strong economy.
The measures taken in the economic sphere are aimed at expanding entrepreneurship based on market economy mechanisms, attracting local and foreign investments, modern technologies and using advanced management practices to create competitive enterprises, create new jobs and increase the country's economic power.
Also, the implementation of the "Contract of the Century", signed in 1994 and laying the foundation for a new stage in the history of the Republic of Azerbaijan, gave a strong impetus to attract foreign investment to the country. Achieving balanced economic development by directing the growing oil and gas revenues to the non-oil sector as a result of the successful implementation of the oil strategy has been one of the most important tasks facing the Azerbaijani state in recent years. In this regard, accelerating the development of the regions has been identified as one of the main goals of the state's economic policy.
The development of the regions in Azerbaijan is the basis of the socio-economic development strategy implemented in our country. The steps taken for the development of the regions have borne fruit over the years. The work done has repeatedly reduced all the negative cases and improved the quality in many areas.
In this regard, the State Program on Socio-Economic Development of the Regions of the Republic of Azerbaijan (2004-2008), first approved by the Decree of the President of the Republic of Azerbaijan No. 24 of February 11, 2004, as well as 2009-2013, 2014- The main objectives of the state programs approved for 2018 and 2019-2023 are sustainable development of the non-oil sector, ensuring balanced development of the country's regions, improving utilities and social infrastructure in the regions, increasing employment and living standards as a result of creating new jobs and enterprises. [2]
State programs for regional development, identified as a priority in the country's socio-economic development strategy and playing an exceptional role in ensuring regional balance through the efficient use of oil and gas revenues, are aimed at increasing business activity, further expanding entrepreneurship in the regions, implementing infrastructure projects and has led to the creation of new enterprises and facilities producing competitive and export-oriented products, and has significantly improved the quality indicators that characterize the well-being of citizens.
Analysis.
Regional development is a complex process that involves a multidisciplinary approach. Without a detailed analysis of successful regional development cases, the implementation of their development systems directly to other regions can lead to the loss of time, capital, and human resources. Regional development is a process that needs to be adapted to specific conditions. Each region has its own identity and unique characteristics. In this respect, there is no entrepreneurial regional policy that can be directly applied to other regions. [3]
We can note that the state's special attention to the development of the regions is mainly aimed at the gradual elimination of unemployment, which has long been a serious social problem through the development of entrepreneurship in Azerbaijan, and the provision of useful employment.
The Decree of the President of the Republic of Azerbaijan dated December 6, 2016 "On approval of strategic roadmaps for the national economy and key sectors of the economy" laid the foundation for sustainable and competitive development of the non-oil sector in the country. If we look at the statistics, we can see that in 2021, the country produced 92857.7 million manat, or 5.6 percent more than the same period last year. It should be noted that it entered the development phase in the period from 2019 to 2020. During this period, according to the Doing Business report, for two years in a row, Azerbaijan became one of the most reformist countries in the world, moving up to 25th place among 190 countries. It is known that the COVID-19 pandemic, as in all countries of the world, has had a negative impact on economic development, and in 2020 our economy fell by 4.3 percent. [4]
Picture 1.
Key economic indicators
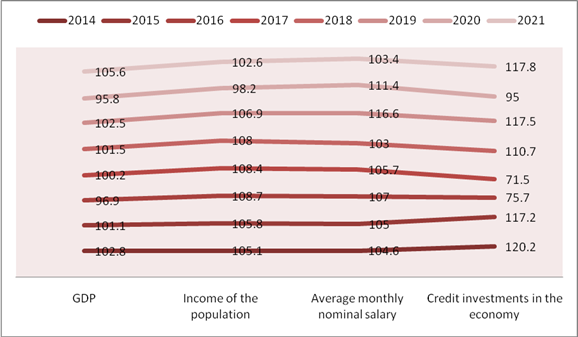
Source: Data of the State Statistics Committee of Azerbaijan.
It should be noted that although the negative effects of the COVID-19 pandemic will continue in 2021, relative improvement in the international situation, support for entrepreneurship, rapid continuation of the vaccination process and easing of the quarantine regime have been observed in economic activity since early 2021. The diagram also shows that economic growth in 2021 was observed. As a result, compared to 2020, GDP in 2021 will increase by 5.6% in real terms and reach 92.9 billion in current prices. manat. Real GDP per capita increased by 5.1% to 9269.3 AZN or 5452.5 US dollars (4272.2 US dollars in the same period of the previous year). In 2021, the nominal income of the country's population increased by 2.6 percent compared to the previous year and amounted to 57181.5 million manat. Per capita income averaged 5708.0 manat. In January-November 2021, the average monthly nominal wage of employees in the country's economy increased by 2.9 percent compared to the corresponding period of 2020 and amounted to 724.1 manat. Salaries in the oil and gas sector amounted to 3150.6 manat, in the non-oil and gas sector 675.4 manat. Salaries of employees of state enterprises were 643.0 manat, and salaries of employees of private enterprises were 819.9 manat. [5]
Another important aspect of socio-economic development in the regions is that the region increases the currency imported by the region and affects the direct export of available natural resources. It is natural resources that allow exploration of underground resources, production, investment and capital-intensive sector. For this purpose, the market for these natural resources has already gone beyond the region and reached the level of world countries. [6]
Reforms in Azerbaijan in 2021, including new economic zoning, structural reforms, application of corporate standards in state-owned enterprises and improvement of the business environment, have achieved positive results in increasing economic efficiency. This year, Azerbaijan has risen from 34th to 28th in the “Doing Business” report, from 44th to 38th in the “Economic Freedom Index” and from 55th to 40th in the “Global Cyber Security Report”. [7]
At present, the issues of investment climate and investment attractiveness are of decisive importance for regional authorities, as the economic growth of regions depends on the volume of investment resources. In the conditions of the economic crisis and fierce competition, it is necessary to develop new methods of increasing the investment attractiveness of the region. [8]
Investment is the allocation of money or another resource, in anticipation of benefits. In an economic crisis, investment in the regional economy is a complex process. This is due to the public production and transformation of investor's income into capital. The volume of investments, their dynamics are characteristics of the regional management system. Using these indicators, you can determine the prospects and rates of regional growth. The macroeconomic impact on the dynamics of investment should also be taken into account. [9]
Also, one of the most successful results of the State Program on socio-economic development of the regions is the formation of a more favorable business and investment environment in the country, the expansion of business opportunities, the effective realization of the production potential of the regions. We know that the essence and conceptual content of the measures taken has led to the liberalization of the economy and the deepening of the principles of the free market. As a result, the share of national entrepreneurs in GDP has reached 85 percent.
From this point of view, it should be noted that the amount of funds allocated from the state budget for the development of entrepreneurship has been increased every year, 324 million manat loans have been provided to 7,000 investment projects through the National Fund for Entrepreneurship Support. 87% of these projects and 70% of loans fall to the regions. At present, the share of the private sector in the agricultural sector, industry, trade, hotel and catering services, construction, transport, communications, production and services is about 70-99 percent. It can be said that entrepreneurs are closely involved in the process of creating new jobs, as well as the formation of more than half of budget revenues. These indicators of socio-economic development are the result of purposeful, correct policy pursued in our country, a solid legal framework has been created in this area, as a result of which today Azerbaijan is recognized in the world as a country with high investment attractiveness. Large investments have been made in various areas of our national economy, both from domestic and foreign sources. Let's look at the investments for 2014-2020.
Table 1.
Investments in the economy 2014-2020.
|
|
2014
|
2015
|
2016
|
2017
|
2018
|
2019
|
2020
|
|
Investments from all sources
(including foreign investments):
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
mlyn.manat
|
21890,6
|
20057,4
|
22706,4
|
24462,5
|
25877,0
|
24986,6
|
22484,0
|
|
mlyn.dollar
|
27907,5
|
19547,2
|
14228,0
|
14213,3
|
15221,7
|
14698,0
|
13225,9
|
|
Foreign
investment:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
mlyn.manat
|
9175,6
|
10998,9
|
16216,1
|
15697,3
|
14002,1
|
12119,5
|
10413,2
|
|
mlyn.dollar
|
11697,7
|
10719,1
|
10161,1
|
9120,5
|
8236,5
|
7129,1
|
6125,4
|
|
Domestic
investments:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
mlyn.manat
|
12715,0
|
9058,5
|
6490,3
|
8765,2
|
11874,9
|
12867,1
|
12070,8
|
|
mlyn.dollar
|
16209,8
|
8828,1
|
4066,9
|
5092,8
|
6985,2
|
7568,9
|
7100,5
|
As can be seen from the table, in 2020 there was an increase of 2.6% compared to 2014. However, the visible decline in 2020 compared to 2018 was 13.1%, which was due to the impact of the pandemic.
Economic polarization is a process that is present at global, national and regional level. Economic activity is extremely spatially concentrated. Cities and developed regions use the agglomeration effect to attract labor and capital, thus achieving more favorable economic conditions than the agrarian region. [10]
At the same time, one of the ways to achieve the socio-economic development of the regions is the development of agriculture in the country. For this reason, the state considers the development of agriculture, as well as ensuring food security of the country as one of the main goals. New mechanisms related to soft loans and subsidies are being developed and implemented.
In particular, it should be noted that the Azerbaijani state and people have achieved a solution to the main problem facing them thanks to the glorious victory in the Great Patriotic War. The Nagorno-Karabakh conflict, which arose as a result of Armenia's occupation policy, has already gone down in history and the territorial integrity of our country has been ensured.
The result
The development of the regions of Azerbaijan is an important part of the strategy of sustainable socio-economic development successfully implemented in the country. Implementation of tasks envisaged in the state programs adopted and successfully implemented in the field of regional development, as well as presidential decrees on additional measures in this field, investment in sustainable development of the non-oil sector in the country increase in investment, creation of new enterprises and jobs, as a result of increasing employment and reducing poverty. The IV State Program for 2019-2023 has already been approved and targets have been set for the near future.
The motives to measure regional development are manifold. But a prominent argument all over the years is that welfare positions of regions or nations may exhibit great disparities which are often rather persistent in nature. These in turn translate into large disparities in living standards.
The objectives of regional development are to improve the development of endangered (agricultural and industrial) regions, encourage employment (through retraining and combating structural unemployment), encouraging youth employment and more. Therefore, regional programs support the development of entrepreneurial culture, entrepreneurship and local economic development, encouraging different innovations.
Источники:
2. State Program of socio-economic development of the regions of the Republic of Azerbaijan of the President of the Republic of Azerbaijan dated February 11, 2004.
3. Todtling F, Trippl M. One size fits all? Towards a differentiated regional innovation policy approach // Research Policy Amsterdam. – 2005. – № 4 (8). – p. 1203–1219.
4. Decree of the President of the Republic of Azerbaijan dated December 6, 2016 "On approval of strategic roadmaps for the national economy and key sectors of the economy".
5. State Statistics Committee of Azerbaijan.
6. Gurbanzadeh A. Regional development model of structural structure Baku // Science. – 2004. – p. 432.
7. Center for Analysis of Economic Reforms and Communication of the Republic of Azerbaijan. [Электронный ресурс]. URL: https://ereforms.gov.az/files/review/pdf/az/faf080a8ac24bac735735e0176e97356.pdf (дата обращения: 25.03.2022).
8. Tayurskaya O.V., Okladnikova D.R., Solodova N. G. Investment In The Regional Economy: Challenges And Prospects. - The European Proceedings of Social & Behavioural Sciences, 2018. – 1161-1168 p.
9. Brymer Rhett, Molloy Janice, Gilbert Brett Human Capital Pipelines // Journal of Management. – 2014. – № 40. – p. 483-508. – doi: 10.1177/0149206313516797.
10. Šabić Dejan, Vujadinovic Snezana Regional development and regional policy // Zbornik radova - Geografski fakultet Univerziteta u Beogradu. – 2017. – p. 463-477. – doi: 10.5937/zrgfub1765463V.
Страница обновлена: 29.03.2024 в 14:35:16
